Submitted by DataRecoveryGroup on
Little do many of us know, RAID technology plays a huge part in our technological lives, and data storage and everything that is built upon it wouldn’t be possible without it. RAID stands for Redundant Array of Independent Disks, and it is represents a major portion of data storage schemes that divide and replicate data among many drives. The dividing and replicating of data is known as striping. The multiple drives then work together as a single unit, and deliver required data as effectively as possible, while storing the data as securely as possible. Let’s back things up a bit and define a few important terms to help us categorize different levels of RAID technology.
Redundancy
This is an engineering term that references the duplication of functions of a system. In other words, the more redundancy, the more copies of your information, and the more protected the system is.
- Parity – This involves assigning a bit to the end of a string of binary code to distinguish it as odd or even (1 or 0). Parity data is used by some RAID levels to increase redundancy and allow someone to fill the missing holes when recovering data.
Performance
Quite literally, this is the level of performance at which the RAID system is able to do what it needs to do. When more backups of data need to be made, or when there is an increased level of redundancy, the less efficient the system becomes.
- Read Performance – The capabilities of reading data off the drives.
- Write Performance – The capabilities of adding data to the drives.
 RAID 0
RAID 0
The upside of RAID 0 is that it is the most efficient way to store data. There is no redundancy of data with RAID 0, and if anything bad happens the data on the drives is gone for good. In order to be useful, RAID 0 technology is used most frequently with the combination of other RAID technologies knownw as nested RAID, as mentioned later.
 RAID 1
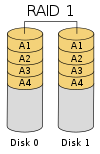
RAID 1
This technique involves at least two drives that replicate each other with the same information, which is also known as disk mirroring. More drives can be used, but the standard is two. Read performance is improved from RAID-0, as information can be read from either disk simultaneously. Write performance depends on the performance of the slower two drives, but it is typically remained unchanged relative to RAID 0 write performance. It is a comonly used technology, and commonly used in nested RAID like RAID 0.
 RAID 2
RAID 2
This technology is stated in theory but is practically never used in the real world as it holds no real commercial value. RAID 2 involves bit level striping with dedicated Hamming-code parity – which is rather outdated.
 RAID 3
RAID 3
Like RAID 2, this technology is rarely used for commercial purposes, but is still superior to RAID 2. Unlike RAID 2 it uses byte level striping and uses dedicated parity instead of Hamming-code parity. Dedicated parity involves storing parity information on only one drive.
 RAID 4
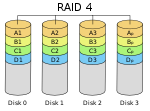
RAID 4
This technology is nearly identical to RAID 5, except the parity data is stored on one drive, like with RAID 3. Each drive operates independently from one another, and uses large stripes to allow that to happen effectively.
 RAID 5
RAID 5
RAID 5 technology distributes the parity data across all drives along with all stored data. This allows write operations to be performed more seamlessly, which makes RAID 5 technology superior to RAID 4.
 RAID 6
RAID 6
This technology is for the most part identical to RAID 5 technology, except that it uses double distributed parity. This allows fault tolerances to be higher, as it protects up to two failed drives.
Nested RAID
Beyond that, there are several levels of nested RAID, aka hybrid RAID, which are combinations of two or more standard level technologies of RAID listed above. This helps gain further redundancy or performance. Popular levels include RAID 10 (1+0), RAID 100 (1+0+0), and RAID 50 (5+0).
Unfortunately, RAID systems can fail, and valuable data can be lost in the process. That’s where we step in. If you’re looking to learn about recovering data from RAID systems, head over to our RAID recovery services page. Our team of data recovery experts would be happy to help identify the problem and get your business back on track as quickly as possible.
